Új berendezés és módszer a kristályosodásnál kialakuló szemcseszerkezet finomításához
Absztrakt
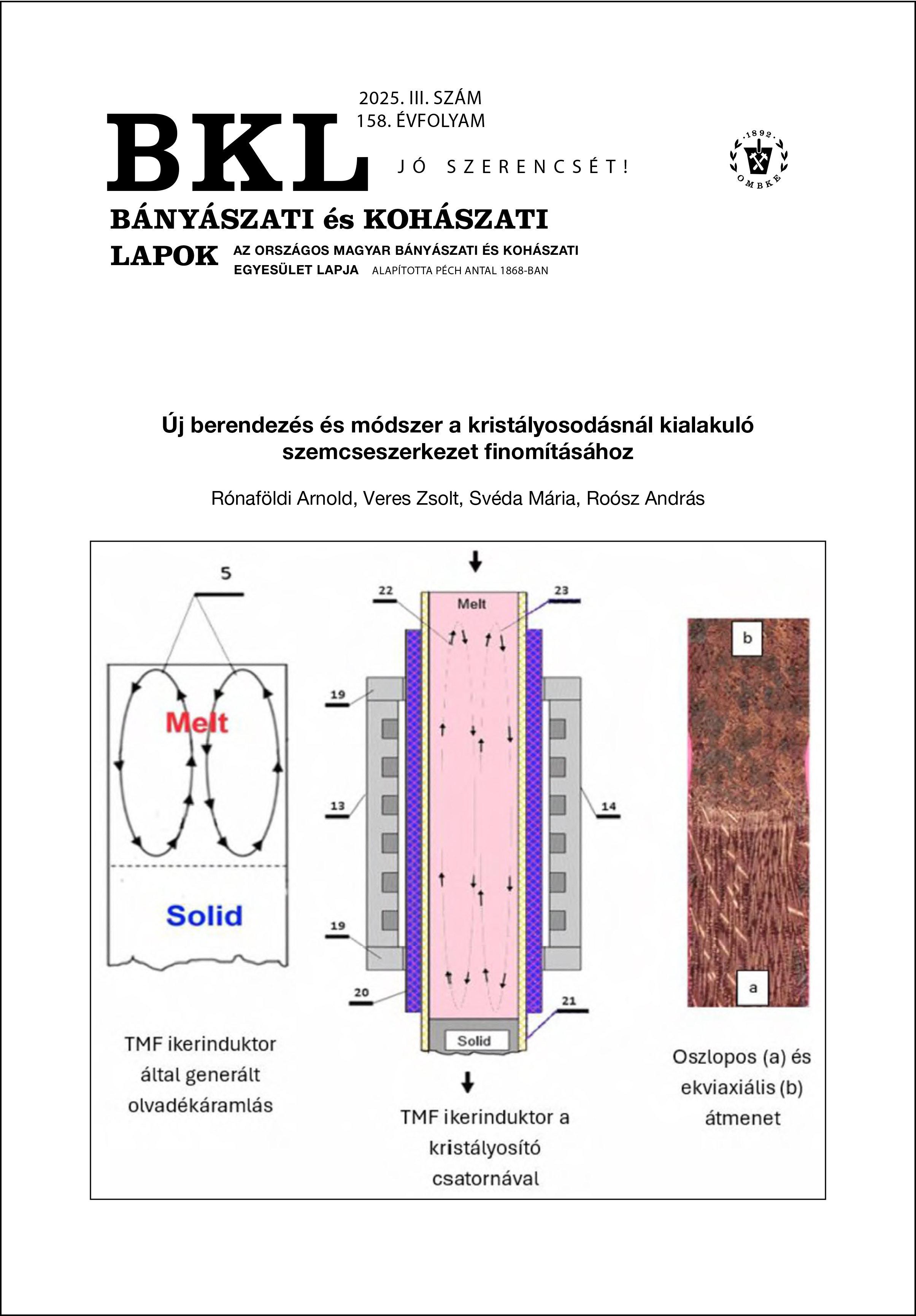
A munka célja egy hatékony mágneses keverőberendezés és keverő módszer megalkotása volt. Mivel a forgó mágneses mező (Rotation Magnetic Field, RMF) általi keverés gyakran erős makrodúsulást eredményez, a keveréshez a haladó mágneses teret (Travelling Magnetic Field, TMF) választottuk. A TMF ikerinduktornak a felépítése jelentősen eltér a hagyományos mágneses keverőktől, mert zárt mágneses áramkörrel rendelkezik. A kifejlesztett ikerinduktorral három különböző mágneses mező állítható elő a keverőhatás vizsgálatára. A mágneses mező erős nyírófeszültséget fejt ki a kristályosodási frontra merőleges áramlásnál azáltal, hogy a fémes olvadék rétegek egy része ellentétes irányban mozog. A TMF ikerinduktort egy kristályosító berendezéssel kombináltuk a különböző ötvözetek egyirányú kristályosításához.
Az ikerinduktorral létrehozott három különböző mágneses térnek a szemcseszerkezetére gyakorolt hatását Al-7%Si-1% és Al-10%Si-0,2%Fe ötvözetekkel hasonlítottuk össze. Kimutattuk, hogy a leghatékonyabb keveredés és ezzel a szemcsefinomítás akkor következik be, amikor a két induktor mágneses tere egymással szemben mozog.
Hivatkozások
Mansoor M, Shahid M.: On the designing, efficiency,and stirring force of an induction coil for the processing of prototype Al based nanocomposites. Journal of Metallurgy. 2014; 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/637031
Sigworth GK, Kuhn TA: Grain refinement of Aluminium casting alloys. AFS Transactions © American Foundry Society, Schaumburg, IL USA. 2007; 1–12. Int. J. Metalcasting 2007; 1: 31–50. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/bf03355416#citeas
Mark Easton, Cameron Davidson, David StJohn:Grain Morphology of As-Cast Wrought Aluminium Alloys. Materials Transactions 2011; 52/5: 842–847.https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.L-MZ201118
Kori SA, Murty BS, Chakraborty M.: Development of an efficient grain refiner for Al-7Si alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2000; 280: 58–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(99)00656-5
Li HT, Xia M, Ph. Jarry, Scamans GM, Fan Z.: Grain refinement in a AlZnMgCuTi alloy by intesive melt shearing: A multi-step nucleation mechanism. J. Cryst. Growth. 2011; 314/1: 285–292. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/337304.pdf
Zimmermann G, Sturz L, Walterfang M, Dagner J.: Effect of melt flow on dendrites growth in Al-Si7-based alloy during directional solidification. Int. J. Cast Metals Research. 2009; 22: 335-338. https://doi.org/10.1179/136404609X368154
Zimmermann G, Vitusevych WT, Sturz L.: Microsturcture formation in AlSi6Cu4 alloy with forced melt flow induced by a rotating magnetic field. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2010; 649: 249–254. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.649.249
Nikrityuk PA, Eckert K, Grundmann R.: A numerical study of unidirectional solidification of a binary metal alloy under influence of a rotating magnetic field. Int. J. Heat and Mass Transfer. 2006; 49/7–8: 1501–1515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2005.08.035
Eckert S, Nikrityuk PA, Räbiger D, Eckert K, Gerbeth G.: Efficient melt stirring using pulse sequences of a rotating magnetic field. Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 2007; 38B/6: 977–988. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-007-9096-4
Veres Zs, Roósz A, Rónaföldi A, Sycheva A, Svéda M: The effect of melt flow induced by RMF on themeso- and micro-structure of unidirectionally solidified Al–7wt.% Si alloy Benchmark experiment under magnetic stirring. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021; 103: 197–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.06.060
Zaïdat K, Ouled-Khachroum T, Vian G, Garnier C, Mangelinck-Noël N, Dupouya MD, Moreau R. Directional solidification of refined A1-3.5wt% Ni under natural convection and under a forced flow driven by a travelling magnetic field. J. Cryst. Growth. 2005; 275/1–2: e1501–e1505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2004.11.182
Su Yan-Qing, Xu Yan-Jin, Zhao Lei, Guo Jing-Jie, Fu Heng-Zhi: Effect of electromagnetic force on melt induced by travelling magnetic field, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010; 20/4: 662–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(09)60195-3
Zou QC, Jie JC, Liu SC, Wang TM, Yin GM, Li TJ: Effect of traveling magnetic field on separation andpurification of Si from Al–Si melt during solidification. Journal of Crystal Growth 2015; 429: 68–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2015.08.015
Qin L, Shen J, Feng Z, Shang Z, Fu H: Microstructure evolution in directionally solidified Fe–Ni alloys under traveling magnetic field. Materials Letters 2014 Jan 15; 115: 155–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2013.10.082
Min Z, Shen J, Feng Z, Wang L, Wang L, Fu H: Effects of melt flow on the primary dendrite spacing of Pb–Sn binary alloy during directional solidification. Journal of Crystal Growth 2011 Apr 1; 320/1: 41–45. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2011.01.013
Qin L, Li Q, Liu W: Modeling and experiments on electromagnetic separation of inclusions from Aluminum melt under combined magnetic field. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering 2014 Aug 1; 43(8): 1793-1797. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-5372(14)60133-8
He Y, Li Q, Liu W: Effect of combined magnetic field on the eliminating inclusions from liquid aluminum alloy. Materials Letters 2011 Apr 30; 65(8): 1226-1228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2011.01.061
Rónaföldi A, Roósz A: Method and equipment for refinement of solidified grain structure. Patent number: HU231169. 19 May 1970.